This topic focuses on comparing the leading cloud providers, namely Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). The objective is to provide an in-depth analysis of the features, services, and performance offered by each provider, enabling businesses and individuals to make informed decisions when choosing a cloud platform.
Introduction to Cloud Computing and the Importance of Cloud Providers
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals manage and store their data. In simple terms, cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services over the internet, including storage, servers, databases, networking, and software. This technology involves the provision of on-demand computing resources that are scalable and flexible. Instead of owning and managing physical infrastructure, users can access computing resources and services on a pay-as-you-go basis, eliminating the need for upfront investments and enabling rapid scalability. Cloud providers play a crucial role in this ecosystem by offering infrastructure, services, and platforms to support diverse computing needs.
Benefits of using cloud providers
The use of cloud providers offers several benefits to organizations and individuals. Firstly, it provides access to a vast range of computing resources without the need for expensive hardware and infrastructure setup. Cloud providers manage the underlying infrastructure, allowing users to focus on their core business objectives.
Secondly, cloud computing enables scalability and flexibility. Users can easily scale their resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency. Additionally, cloud providers offer a wide array of services and solutions, including data storage, compute power, databases, networking, and security tools.
Thirdly, cloud computing promotes collaboration and remote work. Cloud-based applications and services can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling teams to work together seamlessly and increasing productivity.
Significance of comparing AWS, Azure, and GCP

Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are the three leading cloud providers in terms of market share, popularity, and service offerings. Comparing these providers is essential to make informed decisions when choosing a cloud platform.
Each provider has its strengths and areas of focus. By conducting a comparative analysis of Azure vs AWS vs Google Cloud Platform, businesses and individuals can assess which provider aligns best with their specific requirements, such as compute services, storage options, networking capabilities, database services, AI and machine learning offerings, security features, and compliance standards.
Overview of AWS, Azure, and GCP
Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS, a subsidiary of Amazon, is the largest cloud computing company and the most dominant player in the market. It offers a wide range of cloud services, including compute power, storage, databases, networking, analytics, machine learning, and IoT solutions. AWS has a vast global infrastructure that spans multiple regions, allowing users to deploy their applications closer to end-users for better performance. Is AWS the best cloud service provider? – It’s a question for us to find out.
Microsoft Azure: Developed by Microsoft, Azure is a comprehensive cloud computing platform that provides infrastructure, platform, and software services. Azure leverages Microsoft’s extensive software ecosystem and integration with popular tools like Microsoft Office, Windows Server, and Active Directory. It offers a wide range of services, including virtual machines, storage, databases, AI, IoT, and developer tools.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP, developed by Google, emphasizes its expertise in data analytics, machine learning, and open-source technologies. GCP provides a broad set of services, including compute, storage, databases, AI, and machine learning. It leverages Google’s global network infrastructure and offers integration with popular Google services such as Google BigQuery, Google Kubernetes Engine, and TensorFlow.
Examples of companies using AWS, Azure, or GCP
Exploring case studies and examples of companies using AWS, Azure, or GCP can provide valuable insights into real-world deployments and use cases. Users can gain a better understanding of how organizations in similar industries have leveraged the capabilities of each provider.
Prominent AWS customers include:
- Expedia
- Netflix
- Coinbase
- Formula 1
- Coca Cola
- Intuit
- Airbnb
- Lyft
- Coursera
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Well-known Azure customers include:
- DAIMLER AG
- McKesson Group
- Asos
- Center of Disease Control (CDC) – US
- National Health Service (NHS) – UK
- HSBC
- Starbucks
- Walgreens
- 3M
- HP
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Renault
Notable GCP customers include:
- Toyota
- Unilever
- Nintendo
- Spotify
- The Home Depot
- Target
- Paypal
- UPS
Market share and popularity of the most popular cloud platforms
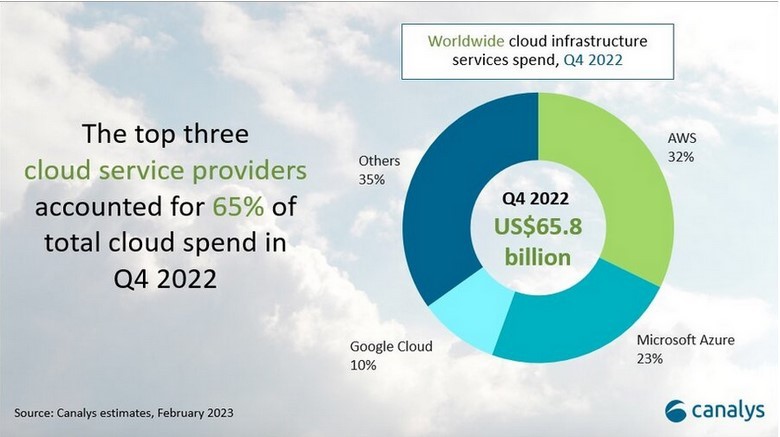
AWS has been a dominant force in the cloud computing market for many years and continues to maintain a significant market share. Azure has emerged as a strong competitor, benefiting from its integration with Microsoft’s existing enterprise software. GCP has also gained traction, particularly in industries that require advanced data analytics and machine learning capabilities.
Key strengths and areas of focus
AWS: AWS offers the most extensive range of services, providing users with a wide variety of options for their computing needs. It has a robust infrastructure and a mature ecosystem, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes. AWS focuses on scalability, flexibility, and global presence.
Pros:
- Most services available, from networking to robotics
- Most mature
- Considered the gold standard in cloud reliability and security
- More compute capacity vs Azure & GCP
- All major software vendors make their programs available on AWS
Azure: Azure’s key strength lies in its integration with Microsoft’s suite of products, making it an attractive choice for organizations already invested in Microsoft technologies. It emphasizes hybrid cloud solutions, allowing businesses to seamlessly integrate their on-premises infrastructure with the cloud.
Pros:
- Easy integration and migrations for existing Microsoft services
- Many services available, including best-in-class AI, ML, and analytics services
- Relatively cheaper for most services vs AWS & GCP
- Great support for hybrid cloud strategies
GCP: GCP differentiates itself with its expertise in data analytics and machine learning. It provides advanced tools and frameworks for data analysis and offers extensive support for open-source technologies. GCP is favored by organizations looking to leverage cutting-edge AI and machine learning capabilities.
Pros:
- Plays nicely with other Google service and products
- Excellent support for containerized workloads
- Global fiber network
Feature Comparison of Cloud Services
The aws, azure, gcp service comparison is critical to understanding their capabilities and suitability for different use cases. Let’s explore the key areas of comparison:
Compute services
All three cloud providers offer a variety of compute options, including virtual machines, containers, and serverless computing platforms. Users can choose the most appropriate compute service based on their specific requirements, performance needs, and budget.
|
Compute services |
||
|
AWS |
AZURE |
GCP |
|
|
|
Storage options
AWS, Azure, and GCP provide object storage, block storage, and file storage solutions. The storage options vary in terms of performance, durability, availability, and pricing models. Users must evaluate the storage services based on their data storage and retrieval needs.
|
Storage options |
||
|
AWS |
AZURE |
GCP |
|
|
|
Networking capabilities
Networking capabilities are crucial for connecting resources within the cloud and integrating with on-premises infrastructure. AWS, Azure, and GCP offer virtual networks, load balancing, content delivery networks (CDNs), and other networking features. However, the implementation and feature sets may differ among the providers.
|
Networking capabilities |
||
|
AWS |
AZURE |
GCP |
| Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) | Azure Virtual Network (VNET) | Cloud Virtual Network |
|
Load Balancing |
||
| Elastic Load Balancer | Azure Load Balancer | Google Cloud Load Balancing |
|
Firewall |
||
| AWS Firewall / Web Application Firewall | Azure Firewall | Google Cloud firewalls |
|
DNS |
||
| Route 53 | Azure DNS | Google Cloud DNS |
|
CDN |
||
| Amazon CloudFront | Azure Content Delivery Network (CDN) | Cloud CDN |
Database services
Databases are fundamental for storing and managing data in the cloud. AWS, Azure, and GCP provide a range of database options, including SQL databases, NoSQL databases, and managed database services. Users should consider factors such as performance, scalability, availability, and compatibility when choosing a database service.
|
Database Services |
||
|
AWS |
AZURE |
GCP |
|
|
|
AI and machine learning offerings
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are increasingly important in various industries. All three providers have robust offerings in this domain, including pre-built models, training platforms, and data analytics tools. Users should assess the available AI and ML services to determine which provider offers the most suitable solutions for their needs.
|
AI & ML |
||
|
AWS |
AZURE |
GCP |
|
|
|
Security and compliance features
Security is a top priority for cloud customers. AWS, Azure, and GCP provide a wide array of security features, including encryption, identity and access management, threat detection, and compliance certifications. Evaluating the security and compliance offerings of each provider is essential to meet regulatory requirements and protect sensitive data.
|
Security |
||
|
AWS |
AZURE |
GCP |
| AWS Security Hub | Azure Security Center | Cloud Security Command Center |
|
Documentation |
||
| Best in class | High quality | High quality |
|
Compliance |
||
| AWS CloudHSM | Azure Trust Center | Google Cloud Platform Security |
Service Portfolio
Available services and solutions offered by each provider
AWS, Azure, and GCP have extensive service portfolios covering various domains. Each provider offers numerous services and solutions, including analytics, IoT, serverless computing, containerization, developer tools, and more. Users should explore the available services to determine which provider aligns with their specific business requirements.
|
Services |
||
|
AWS |
AZURE |
GCP |
|
DevOps |
||
|
|
|
|
AI & ML |
||
|
|
|
|
IoT |
||
|
|
|
|
AR & VR |
||
| Amazon Sumerian | Azure Mixed Reality (Spatial Anchors/Remote Rendering) | ARCore |
|
Game Development |
||
| Amazon GameLift | Azure PlayFab | – |
|
Business Analytics |
||
| Amazon Quicksight | Azure Power BI | Looker |
|
End-User Computing |
||
| Amazon Workspaces | Azure Virtual Desktop | – |
|
Robotics |
||
| AWS RoboMaker | – | – |
Differentiation in service offerings
While there may be overlap in certain services, AWS, Azure, and GCP differentiate themselves by focusing on specific areas. For example, AWS has a broad service offering with a strong emphasis on infrastructure scalability. Azure emphasizes hybrid cloud capabilities, while GCP emphasizes data analytics and machine learning.
Industry-specific solutions
All three providers cater to specific industries by offering industry-specific solutions and compliance certifications. Users with industry-specific requirements, such as healthcare or finance, should assess which provider offers the most comprehensive solutions and compliance frameworks for their sector.
AWS: Amazon Web Services has a wide range of industry-specific solutions and certifications to address specific requirements. AWS offers solutions tailored for sectors such as healthcare, finance, retail, media, manufacturing, and more. For example, AWS has HIPAA compliance for healthcare data, PCI DSS compliance for secure payment processing, and GDPR compliance for data protection. AWS provides specialized services like Amazon Elastic Transcoder for media processing, Amazon Connect for customer contact centers, and Amazon Personalize for personalized recommendations.
Azure: Microsoft Azure also offers a comprehensive set of industry-specific solutions and compliance certifications. Azure has specialized solutions for sectors like healthcare, finance, government, retail, and more. Azure provides services such as Azure API for FHIR for healthcare interoperability, Azure Machine Learning for predictive analytics, and Azure Government for secure government cloud deployments. Azure holds certifications like HIPAA, HITRUST, FedRAMP, and ISO 27001 to meet regulatory requirements across industries.
GCP: Google Cloud Platform also provides industry-specific solutions and compliance certifications, although its offerings may be relatively more focused on specific industries. GCP offers solutions for sectors like healthcare, finance, retail, media, and gaming. For example, GCP has the Healthcare API for interoperability, BigQuery for data analytics, and Media Solutions for media processing and delivery. GCP holds certifications such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, ISO 27001, and SOC 2 to ensure compliance with industry regulations.
When selecting a cloud provider for industry-specific requirements, businesses should evaluate the offerings, features, and certifications provided by each provider in the relevant sector. Factors to consider include the availability of specialized services, compliance with industry standards, data security measures, scalability, reliability, and overall cost-effectiveness. It is recommended to consult with industry experts or engage with representatives from each provider to determine the best fit for specific industry needs.
Pricing Models and Cost Comparisons of Cloud Service Providers
AWS, Azure, and GCP have different pricing models and structures. Understanding the pricing options, such as on-demand instances, reserved instances, and spot instances, is crucial for optimizing costs. Users should consider factors such as compute usage, storage requirements, data transfer, and additional services when comparing costs.
According to the IT community, Microsoft Azure is widely considered to have the most affordable on-demand pricing among cloud providers, with Amazon falling somewhere in the middle. However, for enterprise customers who already use Microsoft services such as Windows, active directory and MS SQL, switching to Azure proves to be much more cost-effective in comparison of cloud platforms from other providers.
Comparison of pricing models
Users can compare the pricing models of AWS, Azure, and GCP to determine which provider offers the most cost-effective options for their specific workload. It is important to analyze the pricing details of compute instances, storage options, data transfer, and any additional services used.
|
Pricing |
||
|
AWS |
AZURE |
GCP |
| Smallest Instance | ||
| In the case of AWS, a very basic instance that includes 2 virtual CPUs and 8 GB of RAM will cost you around US$69 per month. | For the same type of instance, i.e., an instance with 2 vCPUs and 8 GB of RAM, in Azure, will cost you around US$70/month. | Compared to AWS, GCP will provide you the most basic instance, containing 2 virtual CPUs and 8 GB of RAM at a 25 percent cheaper rate. So, it will cost you around US$52/month. |
|
Largest Instance |
||
| The largest instance offered by AWS that includes 3.84 TB of RAM and 128 vCPUs will cost you around US$3.97/hour. | The largest instance offered by Azure includes 3.89 TB of RAM and 128 vCPUs. It costs around US$6.79/hour. | GCP takes the lead here with its largest instance that includes 3.75 TB of RAM and 160 vCPUs. It will cost you around US$5.32/hour. |
It is worth mentioning that AWS recently introduced a billing system based on per-minute usage. On the other hand, Azure already offers per-minute billing, while Google Cloud provides even more granular per-second billing options, which can lead to greater cost savings compared to AWS or Azure. Moreover, Google Cloud offers a range of discounts that can help customers save up to 50 percent in certain cases, surpassing the savings potential of AWS. Gartner, a leading research and advisory company, has noted that Google Cloud offers significant discounts and highly flexible contracts in an effort to attract customers and win project bids.
Cost management tools and resources
Each provider offers cost management tools and resources to help users optimize their cloud spending. Users can monitor usage, set budget limits, and leverage recommendations to control costs. Understanding the available cost management features is essential for efficient cloud cost management.
AWS Cost Management
AWS provides a comprehensive suite of cost management tools and resources, including:
- AWS Cost Explorer: This tool allows users to visualize, analyze, and forecast their AWS costs and usage patterns. It provides cost breakdowns by services, regions, and tags, enabling users to identify cost drivers.
- AWS Budgets: Users can set up budget limits and receive alerts when costs exceed predefined thresholds. It helps in monitoring spending and controlling costs.
- AWS Cost Anomaly Detection: This feature uses machine learning to detect anomalies in cost and usage patterns, helping users identify unexpected cost increases or spikes.
- AWS Cost and Usage Reports: Detailed reports that provide comprehensive insights into cost and usage data, allowing users to perform in-depth analysis and custom reporting.
Azure Cost Management and Billing
Azure offers several tools and resources for cost management and billing, including:
- Azure Cost Management: This tool provides cost analysis, budgeting, and forecasting capabilities. Users can track and optimize costs across Azure services and third-party clouds.
- Azure Budgets: Similar to AWS, users can set budget limits and receive alerts to monitor spending and control costs effectively.
- Azure Advisor: This tool provides recommendations to optimize costs, enhance performance, and improve security and reliability based on Azure best practices.
- Azure Cost Management and Billing APIs: These APIs allow users to programmatically access cost and usage data, automate billing processes, and integrate with other systems.
GCP Cost Management
Google Cloud Platform offers cost management tools and resources, including:
-
- Google Cloud Console: Users can monitor costs, view detailed billing reports, and analyze spending patterns using the web-based console.
- Google Cloud Billing Catalog API: This API enables programmatic access to billing data, allowing users to automate billing processes and integrate with other systems.
- Google Cloud Pricing Calculator: A tool that helps estimate costs for GCP services based on usage patterns and configuration parameters.
- Commitment-Based Discounts: GCP offers discounts for sustained usage through committed-use contracts, providing cost savings for long-term commitments.
- GKE cost optimization insights: analytic tool that helps is a feature that helps you identify and fix resource usage inefficiencies in your Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) clusters.
It is important for users to familiarize themselves with the available cost management tools and resources provided by each cloud provider. By leveraging these tools effectively, users can monitor their cloud spending, set budget limits, receive alerts, analyze usage patterns, and receive recommendations to optimize costs and maximize the value of their cloud investments.
Case studies and examples illustrating cost differences
Examining real-world case studies or examples can provide insights into the cost differences between AWS, Azure, and GCP. Analyzing these examples can help organizations understand the potential cost implications of choosing a particular provider based on their specific use case and workload.
Case Study: Dropbox Migration from AWS to GCP
Dropbox, a cloud storage and collaboration platform, migrated from AWS to GCP. The motivation behind this move was to reduce costs and leverage GCP’s cost-effective offerings. By migrating to GCP, Dropbox achieved significant cost savings, estimated to be around 25% over a two-year period. The company reported that GCP’s pricing models and discounts were more favorable for their specific workload, resulting in substantial cost reduction.
Case Study: Lyft’s Multi-Cloud Approach
Lyft, the ride-sharing platform, adopted a multi-cloud strategy by leveraging both AWS and GCP. Lyft utilized AWS for its production workloads, while GCP was used for data analytics and machine learning. The multi-cloud approach allowed Lyft to optimize costs by using the most cost-effective services from each provider based on specific workload requirements. By taking advantage of the cost-effective services and pricing options offered by both AWS and GCP, Lyft was able to manage costs efficiently.
Example: Azure Hybrid Benefit
Azure offers the Azure Hybrid Benefit program, which allows customers with existing on-premises licenses to utilize them on Azure virtual machines (VMs) without additional licensing costs. This benefit can result in substantial cost savings for organizations that have invested in Microsoft software licenses, as they can apply their existing licenses to Azure VMs and avoid paying for new licenses.
Example: AWS Spot Instances
AWS provides Spot Instances, which allow users to bid on spare EC2 capacity at significantly discounted prices compared to On-Demand Instances. Spot Instances can be particularly cost-effective for workloads that have flexible start and end times, as users can take advantage of the lower prices during periods of excess capacity. This pricing model enables significant cost savings, especially for non-time-sensitive workloads or those that can tolerate interruptions.
Example: GCP Sustained Use Discounts
GCP offers Sustained Use Discounts, which automatically apply discounted pricing to VM instances that are continuously running for a significant portion of the month. As the usage of instances increases, the discounts also increase, resulting in cost savings for long-running workloads. This pricing model incentivizes sustained usage and can lead to considerable cost reductions for organizations with workloads that have consistent and prolonged usage patterns.
Performance and Scalability

Infrastructure availability and reliability
Infrastructure availability and reliability are critical factors to consider when selecting a cloud provider. AWS, Azure, and GCP have robust global infrastructures with redundant data centers to ensure high availability and minimize downtime. Users should evaluate the providers’ service level agreements (SLAs) and uptime records to assess their reliability.
AWS Infrastructure
Amazon Web Services operates a vast global infrastructure that spans multiple regions and availability zones (AZs). A region consists of multiple physically separated AZs, each equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking. This architecture ensures that if one AZ experiences an issue, services can automatically failover to another AZ within the same region. AWS has a strong track record of uptime and has achieved high availability for many years.
- Amazon Web Service has 25 geographic regions with 81 availability zones. 218+ edge locations, and 12 Regional Edge Caches.
Azure Infrastructure
Microsoft Azure also maintains a global infrastructure across multiple regions and data centers. Each region consists of at least two or more data centers, and like AWS, these data centers are equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking. Azure uses Availability Sets and Availability Zones to distribute resources across multiple data centers within a region. This setup provides redundancy and helps ensure high availability. Azure has a robust SLA guaranteeing a certain level of uptime for its services.
- Microsoft Azure runs 60+ regions with a minimum of three availability zones in each region with more than 116 edge locations.
GCP Infrastructure
Google Cloud Platform operates a global infrastructure with multiple regions and availability zones. GCP data centers are designed with redundant power, cooling, and networking to ensure high availability. GCP uses the concept of regions and zones, where regions consist of multiple zones that are isolated from each other. GCP services are designed to be highly available, and Google boasts a strong track record of reliability and uptime.
- Google Cloud Platform has 27 cloud regions with 82 zones and 146 edge locations.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
All three cloud providers offer SLAs that guarantee a certain level of service availability. These SLAs specify the percentage of uptime and provide compensation in the event of service disruptions. For example, AWS offers SLAs for services like EC2, S3, and RDS, with uptime commitments ranging from 99.95% to 99.99%. Azure and GCP also provide SLAs for various services with similar uptime commitments.
Uptime Records
The cloud providers maintain a transparent approach regarding their uptime records. While the exact figures may vary over time, they generally strive to achieve high uptime levels. It is recommended for users to review historical uptime data and service outage reports from each provider to gain insights into their track record.
To evaluate the reliability of a cloud provider, users should consider factors such as the design of their infrastructure, the number of regions and availability zones, their SLAs, and historical uptime records. It’s also important to note that no infrastructure is entirely immune to occasional disruptions, and organizations should implement appropriate redundancy and disaster recovery strategies to mitigate potential risks.
Scalability options and limitations
Scalability is one of the main advantages of cloud computing. Users should evaluate the scalability options provided by AWS, Azure, and GCP, including the ability to scale compute resources, storage capacity, and networking capabilities. It is also important to understand any limitations or constraints on scalability imposed by each provider.
AWS:
- Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling: AWS provides EC2 Auto Scaling, which allows you to automatically scale compute resources based on predefined conditions or metrics. You can scale instances horizontally to handle varying workloads efficiently.
- Amazon RDS Scalability: Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) offers options for scaling database instances vertically (increasing compute and memory resources) and horizontally (using read replicas for read-heavy workloads).
- Amazon S3 Scalability: Amazon S3 provides virtually unlimited storage capacity, allowing you to scale your storage needs without worrying about infrastructure limitations.
- Limitations: AWS imposes certain limitations on scalability, such as maximum instance sizes, regional availability of certain instance types, and maximum number of resources that can be provisioned per account. These limitations can vary depending on the specific service and instance type being used.
Azure:
- Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets: Azure offers Virtual Machine Scale Sets, which enable you to automatically scale a group of virtual machines based on predefined scaling rules or metrics. This allows for horizontal scaling of compute resources.
- Azure SQL Database Elastic Pools: Azure SQL Database provides elastic pools, which allow you to share resources across multiple databases. This helps in scaling database workloads efficiently.
- Azure Storage Scalability: Azure Blob Storage and Azure Files offer virtually unlimited storage capacity, enabling you to scale your storage needs without worrying about limitations.
- Limitations: Azure has certain limitations on scalability, such as maximum number of virtual machine instances per subscription, regional availability of certain instance types, and limits on database size or transactions per second. These limitations may vary depending on the specific service and subscription type.
GCP:
- Google Compute Engine Autoscaler: GCP provides Autoscaler, which allows for automatic scaling of virtual machine instances based on predefined criteria or metrics. It enables you to scale compute resources horizontally as per workload demands.
- Google Cloud SQL Vertical Scaling: Google Cloud SQL offers the ability to scale database instances vertically by increasing CPU and memory resources to handle growing workloads.
- Google Cloud Storage Scalability: Google Cloud Storage provides virtually unlimited storage capacity, allowing you to scale your storage requirements without constraints.
- Limitations: GCP has certain limitations on scalability, such as maximum number of virtual machine instances per project, regional availability of certain instance types, and limits on database size or concurrent connections. These limitations can vary depending on the specific service and project configuration.
It’s important to review the specific scalability options and limitations of each cloud provider based on your workload requirements and growth projections. Additionally, consider factors like scalability automation, cost implications, and performance considerations when evaluating the scalability capabilities of AWS, Azure, and GCP.
Real-world use cases highlighting performance aspects
Analyzing real-world use cases and customer experiences can provide practical insights into the performance aspects of AWS, Azure, and GCP. Understanding how organizations in similar industries or with similar workloads have leveraged the performance capabilities of each provider can guide decision-making.
- Netflix: Netflix, a popular streaming service, migrated its infrastructure from its own data centers to the cloud. Initially, Netflix used AWS for its cloud services but later expanded to utilize both Azure and GCP as well. By adopting a multi-cloud strategy, Netflix was able to optimize costs by taking advantage of the different pricing models and services offered by each provider. This allowed them to achieve better cost-efficiency and flexibility in managing their infrastructure.
- Lyft: Lyft, a ride-sharing company, primarily used AWS for its cloud services. However, in 2020, Lyft announced a multi-year partnership with Azure to migrate their workload to the Azure cloud platform. This strategic decision was driven by cost considerations, as Lyft believed that Azure offered a more cost-effective solution for their specific requirements. The partnership aimed to leverage Azure’s scalability and cost optimization capabilities to enhance Lyft’s operational efficiency.
- Pokémon GO: When Pokémon GO, a popular mobile game, experienced unprecedented global success, its infrastructure faced scalability challenges. Niantic, the company behind the game, relied on GCP’s global network and infrastructure to handle the massive influx of players. The decision to use GCP was influenced by factors such as cost-effectiveness, reliability, and the ability to quickly scale resources up and down based on demand.
- Epic Games: Epic Games, the creator of the popular game Fortnite, initially relied on AWS for its cloud infrastructure needs. However, in 2020, Epic Games announced a partnership with GCP to leverage its global network and low-latency services. The motivation behind this move was to optimize costs while ensuring a high-quality gaming experience for Fortnite players worldwide.
These case studies highlight how companies evaluate cost differences between cloud providers based on their specific workloads, scalability requirements, and global reach. It’s important to note that cloud services cost comparisons can vary depending on factors such as resource utilization, geographic location, and the pricing models employed by each provider. Conducting a thorough analysis and considering real-world case studies can help organizations make informed decisions about which cloud provider aligns best with their cost objectives.
Integration and Interoperability
Integration with other services and platforms
Integration with existing services and platforms is essential for a seamless cloud adoption process. Google Cloud vs Azure vs Amazon Web Services offer integrations with popular tools, frameworks, and services, such as developer tools, data analytics platforms, and third-party applications. Users should evaluate the compatibility and ease of integration with their existing ecosystem.
AWS:
- AWS Marketplace: AWS Marketplace provides a wide range of third-party software and services that can be seamlessly integrated with AWS resources. This includes developer tools, security solutions, machine learning frameworks, and more.
- AWS SDKs and APIs: AWS offers Software Development Kits (SDKs) and Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) for various programming languages, making it easier to integrate AWS services into your applications and existing workflows.
- AWS Management Tools: AWS provides management tools like AWS CloudFormation, AWS Command Line Interface (CLI), and AWS Management Console, which enable seamless integration with your existing infrastructure and workflows.
- Developer Tools: AWS supports popular developer tools and frameworks such as AWS CodeDeploy, AWS CodePipeline, and AWS CodeCommit, allowing for streamlined development, testing, and deployment processes.
Azure:
- Azure Marketplace: Azure Marketplace offers a wide array of pre-built applications, services, and solutions that can be integrated into your Azure environment. These include virtual machine images, APIs, and managed services from third-party vendors.
- Azure SDKs and APIs: Azure provides SDKs and APIs in multiple programming languages, allowing developers to integrate Azure services into their applications and workflows seamlessly.
- Azure DevOps: Azure DevOps provides a comprehensive set of tools and services for application development, testing, and deployment. It offers integration with popular developer tools like Visual Studio and GitHub for smooth integration into existing development workflows.
- Azure Data Services: Azure provides integration with various data analytics platforms such as Azure Synapse Analytics, Azure Databricks, and Azure HDInsight. This enables seamless integration of data analytics and machine learning capabilities into your existing data workflows.
GCP:
- Google Cloud Marketplace: Google Cloud Marketplace offers a diverse range of third-party solutions that can be integrated into your GCP environment. These include machine learning models, APIs, and enterprise applications.
- GCP SDKs and APIs: GCP provides SDKs and APIs in multiple programming languages, making it easy to integrate GCP services into your applications and workflows.
- Google Cloud Developer Tools: GCP offers developer tools such as Cloud Build, Cloud Source Repositories, and Cloud Debugger, which integrate with popular developer environments and version control systems, enabling seamless development and deployment workflows.
- Big Data and Machine Learning: GCP provides integration with various data analytics and machine learning platforms, such as BigQuery, Cloud Dataflow, and AI Platform. This allows for seamless integration of data processing and machine learning capabilities into your existing workflows.
When assessing the integration capabilities, it’s important to consider the compatibility, ease of integration, and documentation provided by each cloud provider for the specific services, platforms, and tools that are critical to your business. Additionally, check for community support, available resources, and partnerships with other technology vendors to ensure a smooth integration process with your existing ecosystem.
Compatibility with common development tools and frameworks
Developers often rely on specific tools and frameworks for application development. Assessing the compatibility of AWS, Azure, and GCP with common development tools, programming languages, and frameworks is crucial to ensure a smooth development and deployment process.
Compatibility with Programming Languages:
- AWS: AWS supports a wide range of programming languages, including Java, Python, Ruby, .NET, Node.js, Go, and more. It provides SDKs and libraries for these languages, making it easy to develop applications that interact with AWS services.
- Azure: Azure also offers support for popular programming languages such as Java, Python, Ruby, .NET, Node.js, PHP, and more. It provides SDKs, tools, and extensions for these languages to facilitate development on the Azure platform.
- GCP: GCP supports multiple programming languages, including Java, Python, Ruby, .NET, Node.js, PHP, and Go. It offers SDKs, client libraries, and developer tools for these languages to enable seamless integration with GCP services.
Compatibility with Development Tools and Frameworks:
- AWS: AWS integrates well with widely used development tools and frameworks such as Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, Visual Studio, and Git. It also supports popular frameworks like Django, Flask, Spring Boot, and many more.
- Azure: Azure provides integration with popular development tools such as Visual Studio, Visual Studio Code, Eclipse, and IntelliJ IDEA. It supports frameworks like .NET, ASP.NET, Spring Boot, Django, and others.
- GCP: GCP offers compatibility with various development tools, including Visual Studio Code, IntelliJ IDEA, Eclipse, and Google Cloud Tools for popular IDEs. It supports frameworks like .NET, Java Spring, Django, Flask, and more.
Containerization and Orchestration:
- AWS: AWS offers Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) and Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) for container management and orchestration. It supports Docker containers and integrates well with tools like Docker, Kubernetes, and AWS Fargate.
- Azure: Azure provides Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) for container orchestration. It also offers Azure Container Instances (ACI) for running containers without managing underlying infrastructure. Azure integrates with tools like Docker, Kubernetes, and Azure DevOps.
- GCP: GCP provides Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) for container management and orchestration. It supports Docker containers and integrates well with Kubernetes, Helm, and other containerization tools.
Serverless Computing:
- AWS: AWS offers AWS Lambda for serverless computing. It supports multiple programming languages, including Node.js, Python, Java, C#, and more.
- Azure: Azure provides Azure Functions for serverless computing. It supports various programming languages, including C#, Java, JavaScript, PowerShell, and Python.
- GCP: GCP offers Google Cloud Functions for serverless computing. It supports Node.js, Python, and Go as the primary programming languages.
When assessing compatibility with development tools and frameworks, it’s crucial to consider the availability of SDKs, libraries, extensions, and community support for the specific tools, languages, and frameworks you rely on. Additionally, review the documentation and resources provided by each cloud provider to ensure a seamless development and deployment experience within your preferred development ecosystem.
Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud considerations
Organizations may opt for a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategy to leverage the strengths of different providers or maintain flexibility. Evaluating the multi-cloud and hybrid cloud capabilities of AWS, Azure, and GCP can help organizations determine the feasibility of their preferred cloud architecture.
Multi-Cloud Capabilities
- AWS: AWS provides robust multi-cloud capabilities, allowing organizations to integrate AWS services with other cloud providers. AWS offers services like AWS Direct Connect and AWS PrivateLink to establish secure and high-bandwidth connections with other cloud environments. Additionally, AWS has partnerships and integrations with various third-party providers, making it easier to manage multi-cloud deployments.
- Azure: Azure also supports multi-cloud deployments by offering Azure ExpressRoute, which enables organizations to establish private and dedicated connections to other cloud providers. Azure provides Azure Arc, a management tool that allows you to manage resources across multiple clouds, including AWS and GCP. Azure’s open-source approach and compatibility with various tools and frameworks make it well-suited for multi-cloud environments.
- GCP: GCP acknowledges the importance of multi-cloud deployments and offers tools like Anthos, which allows you to manage applications across multiple clouds, including AWS and Azure. Anthos provides a consistent platform and management experience, enabling organizations to deploy and manage applications seamlessly across different cloud environments. GCP’s open-source mindset and focus on hybrid cloud solutions make it a viable option for multi-cloud architectures.
Hybrid Cloud Capabilities
- AWS: AWS supports hybrid cloud deployments through services like AWS Outposts and AWS Snow Family. AWS Outposts extends AWS infrastructure and services to on-premises data centers, enabling a consistent hybrid cloud experience. The AWS Snow Family offers physical devices for secure data transfer between on-premises environments and AWS.
- Azure: Azure provides Azure Arc, which enables you to extend Azure services to on-premises data centers, other clouds, and edge environments. It allows you to manage and govern resources across hybrid environments using Azure’s familiar tools and policies. Azure also offers Azure Stack, a solution for running Azure services on-premises, providing a seamless hybrid cloud experience.
- GCP: GCP supports hybrid cloud deployments through Anthos, which enables you to manage applications across on-premises, multi-cloud, and edge environments. Anthos provides a consistent development and operations experience, allowing you to build, deploy, and manage applications seamlessly across hybrid cloud architectures.
When evaluating multi-cloud and hybrid cloud capabilities, consider factors such as the availability of dedicated connectivity options, compatibility with existing infrastructure and management tools, support for workload mobility, and the ability to maintain consistency and governance across different environments. It’s crucial to review the documentation and resources provided by each cloud provider to assess the suitability of their offerings for your specific multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategy.
Support and Documentation
Support options and response times
Support options and response times vary among AWS, Azure, and GCP. Users should assess the available support channels, such as documentation, knowledge bases, forums, and direct support, as well as the guaranteed response times for critical issues.
AWS Support:
- Support Tiers: AWS offers different support tiers, including Basic, Developer, Business, and Enterprise. Each tier provides different levels of access to support resources, including documentation, whitepapers, and AWS Trusted Advisor.
- Support Channels: AWS provides support through various channels such as documentation, forums, community-driven support, and direct support. Users can access the AWS Support Center for submitting support cases and obtaining personalized assistance.
- Response Times: AWS offers different response time targets based on the severity level of the support case. For example, for the highest severity level (severe production system impairment), AWS aims to provide an initial response within 15 minutes.
Azure Support:
- Support Plans: Azure offers different support plans, including Free, Developer, Standard, and Professional Direct. Each plan offers varying levels of support, access to resources, and guaranteed response times.
- Support Channels: Azure provides support through documentation, knowledge bases, community forums, and direct support options. Users can submit support tickets through the Azure portal or access the Azure Support Center for assistance.
- Response Times: Azure’s support plans specify different response times based on the severity of the support case. For example, for the highest severity level (business-critical impact), Azure aims to provide an initial response within one hour.
GCP Support:
- Support Packages: GCP offers different support packages, including Free, Silver, Gold, and Platinum. Each package provides varying levels of support, access to resources, and response time targets.
- Support Channels: GCP offers support through documentation, knowledge bases, community forums, and direct support options. Users can access the GCP Support Center to submit support cases and seek assistance.
- Response Times: GCP’s support packages outline different response time targets based on the severity of the support case. For example, for the highest severity level (business-critical impact), GCP aims to provide an initial response within 15 minutes.
Documentation, knowledge base, and community resources
The availability of comprehensive documentation, knowledge bases, and community resources is essential for users to learn and troubleshoot effectively. Evaluating the quality and accessibility of the documentation and community resources provided by each provider can help users make informed decisions.
AWS
- Documentation: AWS provides extensive documentation covering a wide range of services, features, and best practices. The AWS Documentation (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/) offers detailed technical information, tutorials, API references, and troubleshooting guides for all AWS services.
- Knowledge Base: The AWS Knowledge Center (https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/) offers a collection of articles, whitepapers, and FAQs to help users troubleshoot common issues, optimize their AWS resources, and stay up to date with best practices.
- Community Resources: The AWS Community (https://aws.amazon.com/community/) is a platform where users can connect with other AWS users, share knowledge, ask questions, and participate in discussions. The community includes forums, blogs, and events where users can learn from and engage with fellow AWS practitioners.
Azure:
- Documentation: Azure provides comprehensive documentation through the Azure Documentation Center (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/). It offers detailed guidance, tutorials, reference materials, and API documentation for Azure services, tools, and features.
- Knowledge Base: The Azure Knowledge Center (https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/resources/knowledge-center/) provides a repository of articles, tutorials, troubleshooting guides, and best practices to help users resolve common issues, optimize their Azure deployments, and gain insights into various Azure capabilities.
- Community Resources: The Azure Community (https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/community/) is a platform that brings together Azure users, experts, and Microsoft employees. It includes forums, blogs, webinars, and events where users can ask questions, share knowledge, and collaborate with the Azure community.
GCP:
- Documentation: GCP offers comprehensive documentation through the Google Cloud Documentation (https://cloud.google.com/docs). It provides detailed information, tutorials, and reference materials covering GCP services, solutions, and APIs.
- Knowledge Base: The Google Cloud Knowledge Center (https://cloud.google.com/resources/knowledge-center/) offers a collection of articles, FAQs, and troubleshooting guides to help users troubleshoot issues, optimize their GCP deployments, and explore best practices.
- Community Resources: The Google Cloud Community (https://cloud.google.com/community) is a platform that connects GCP users, developers, and experts. It includes community forums, blogs, meetups, and events where users can interact, share knowledge, and learn from each other.
When evaluating cloud providers, consider exploring their documentation, knowledge bases, and community resources to assess the quality, depth, and accessibility of the available resources. These resources can serve as valuable references for learning, troubleshooting, and staying updated with the latest advancements in cloud computing.
Training and certification programs
Training and certification programs offered by AWS, Azure, and GCP enable individuals and organizations to enhance their cloud skills and demonstrate expertise. Users can assess the available training resources, certification paths, and professional development opportunities to support their cloud journey.
AWS:
- Training Resources: AWS Training and Certification provides a comprehensive set of training resources, including instructor-led classes, digital training courses, and learning paths. These resources cover a wide range of topics, from core AWS services to specialized areas like machine learning and database management. Visit the AWS Training and Certification website (https://aws.amazon.com/training/) to explore the available training options.
- Certification Paths: AWS offers a range of certifications that validate technical cloud skills at different levels. These certifications include AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner, AWS Certified Solutions Architect, AWS Certified Developer, and many more. For details on AWS certifications, exam guides, and preparation resources, visit the AWS Certification website (https://aws.amazon.com/certification/).
Azure:
- Training Resources: Microsoft Learn is a free platform that offers interactive and self-paced learning resources for Azure. It provides a variety of learning paths, modules, and hands-on labs to help users build Azure skills. Visit the Microsoft Learn website (https://docs.microsoft.com/learn/azure/) to explore the available Azure training resources.
- Certification Paths: Azure offers role-based certifications that validate skills in areas like Azure Administration, Azure Development, and Azure Solutions Architecture. These certifications include Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator Associate, Microsoft Certified: Azure Developer Associate, Microsoft Certified: Azure Solutions Architect Expert, and more. For information on Azure certifications, exam details, and preparation materials, visit the Azure Certification website (https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/training/certification/).
GCP:
- Training Resources: Google Cloud Learning offers a variety of training options, including online courses, hands-on labs, and interactive quests. These resources cover GCP services, data analytics, machine learning, and more. Explore the available GCP training resources on the Google Cloud Learning website (https://cloud.google.com/training).
- Certification Paths: GCP offers certifications that validate skills in areas like Cloud Architecture, Data Engineering, and Machine Learning. These certifications include Google Cloud Certified – Associate Cloud Engineer, Google Cloud Certified – Professional Data Engineer, Google Cloud Certified – Professional Cloud Architect, and others. For information on GCP certifications, exam guides, and preparation resources, visit the Google Cloud Certification website (https://cloud.google.com/certification).
By leveraging the training and certification programs offered by AWS, Azure, and GCP, individuals and organizations can enhance their cloud skills, stay up to date with the latest technologies, and demonstrate their expertise in the respective cloud platforms. Explore the provided links to access the training resources, certification details, and preparation materials for each cloud provider.
Conclusion and Recommendations
After conducting a comparative analysis of AWS, Azure, and GCP, it becomes clear that each provider has its strengths and areas of expertise. AWS offers a comprehensive range of services, Azure excels in hybrid cloud capabilities, and GCP focuses on data analytics and machine learning.
Factors to consider when choosing a cloud provider
When choosing a cloud provider, several factors need to be considered, including specific requirements, service offerings, pricing models, performance capabilities, integration options, support and documentation, and real-world use cases. Organizations should align their needs with the strengths of each provider to make an informed decision.
Recommendations based on specific use cases or requirements
Based on specific use cases or requirements, the following recommendations can be made:
- For organizations heavily invested in Microsoft technologies, Azure provides seamless integration and hybrid cloud capabilities.
- For businesses seeking a wide range of services and global scalability, AWS offers a mature and comprehensive platform.
- For data-driven organizations focusing on advanced analytics and machine learning, GCP provides cutting-edge tools and expertise. Also GCP provides advanced and feature-rich GKE(Google Kubernetes service) which have more advanced level usability than AWS or Azure.
Ultimately, the choice of cloud provider depends on the unique needs and priorities of each organization or individual. Conducting thorough research, evaluating the specific requirements, and considering the comparative analysis presented here will help in making an informed decision.